Forest coverage
Canada’s forests cover 347 million hectares of land and make up nearly nine per cent of world’s total forest area. Canada is the third-most forest country in the world by area.
With nearly 10 hectares/person, people living in Canada enjoy more forest area per person than most other countries in the world, over 17 times the world average.
Nearly 30 million hectares (or about nine per cent) of Canada’s forests are in legally established protected areas.
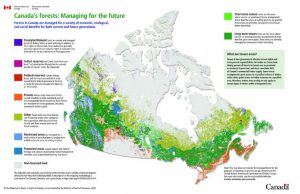
Forest regions
Boreal
Approximately 80 per cent of Canada’s forested land is in the immense boreal forest region, swinging in an arc south from the Mackenzie River Delta and Alaskan border to northeast British Columbia. Across northern Alberta and Saskatchewan, through Manitoba, Ontario and Québec, terminating in northern Newfoundland on the shores of the Labrador Sea.
The northern boreal region consists of open forest with trees growing farther apart and smaller in size as the forest stretches towards the tundra, where only dwarf specimens persist.
The southern boreal region includes a denser, closed forest which. At its southwest boundary in the Prairie provinces, gives way to a transitional zone dominated by poplar.
Known as the aspen grove, this part of the forest thins out into open, almost treeless prairie. White and black spruce are the principal species of the predominantly coniferous boreal forest, but other conifers (e.g., balsam fir, jack pine and tamarack) also have a wide distribution.
There is a mixture of broad-leaved trees in the region, including white birch, balsam poplar and the wide-ranging trembling aspen.
Acadian
Closely related to the Great Lakes-St Lawrence Forest Region. This region covers Nova Scotia, Prince Edward Island and a large portion of New Brunswick.
Red spruce, balsam fir, yellow birch and sugar maple are to commonly found in this region along with black spruce, white and grey birch, red oak, white elm, black ash, beech, red maple, trembling aspen and balsam poplar.











