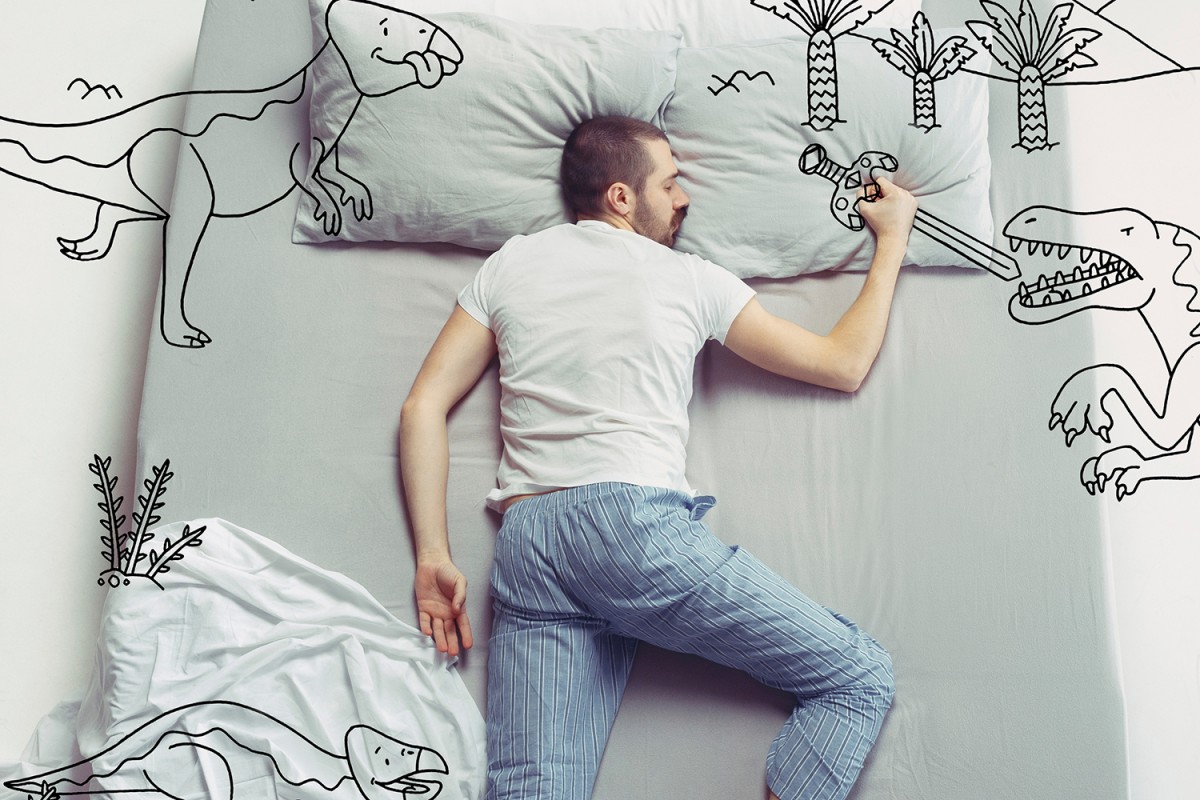
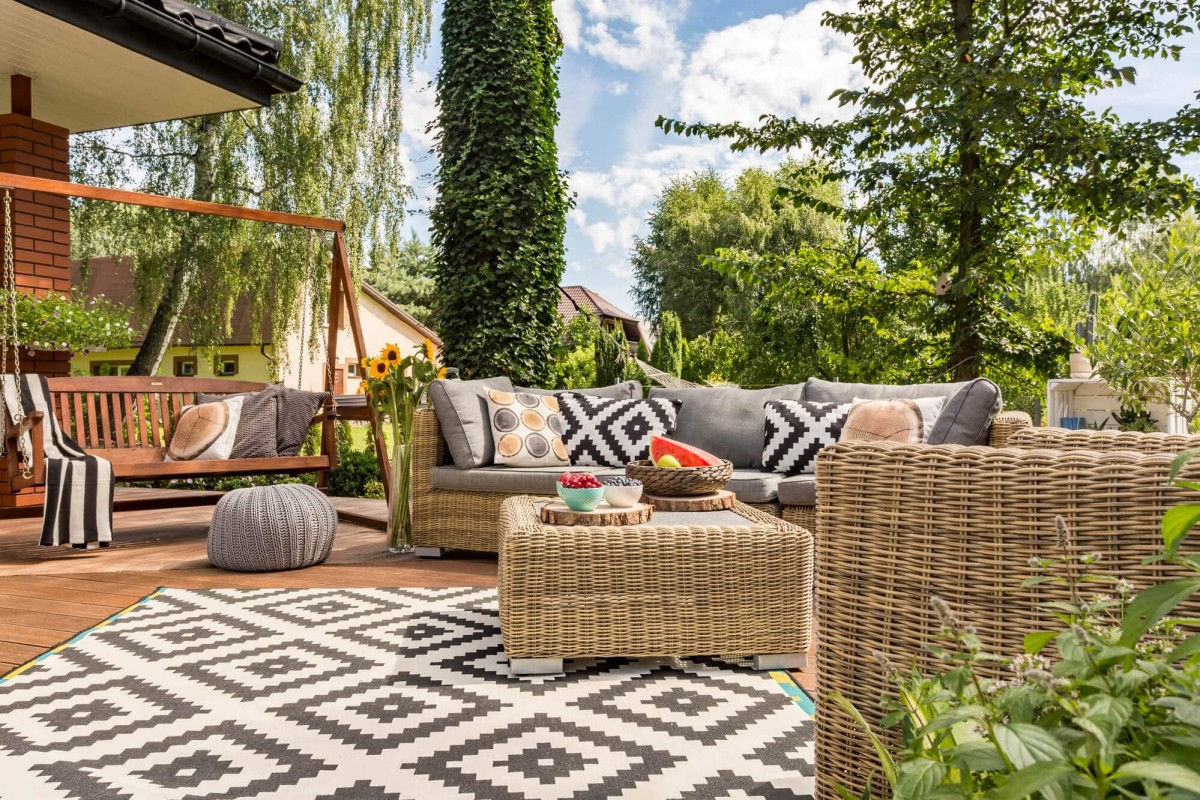
1. Remember
Dreams tap memories stored in connections between brain cells, which the hippocampus tracks as they form. At night it directs neurons to replay recollections, facilitating long-term storage. That could be why reality seeps into our visions—but not why they tend to warp reality.
2. Envision
Our most vivid imaginings occur during the REM phase of sleep. Activity increases in brain regions that control movement and process optical inputs, like the visual and motor cortices, which likely create what we “see” and “do” in slumber. It’s not clear what triggers these areas at night.
3. Feel
The almond-shaped amygdala helps generate feelings like fear, anger, and anxiety. It and other emotional domains are more rowdy during REM sleep, which could explain why strong reactions happen frequently when we doze. We may rely on this process to dull the sting of difficult memories.
4. Decide
Despite their disjointed nature, dreams still contain semi rational thoughts, likely thanks to areas supporting conscious cognition. The anterior, or front, portion of the cingulate, a semicircle in the brain’s center, influences motivation and decision-making—and can switch on while we’re snoozing.
5. Escape
During REM, neuroscientists see suppression of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, which is critical for executive functions like directing attention, solving problems, and reasoning. This might help explain why we rarely realize we’re asleep, despite some outlandish scenarios.