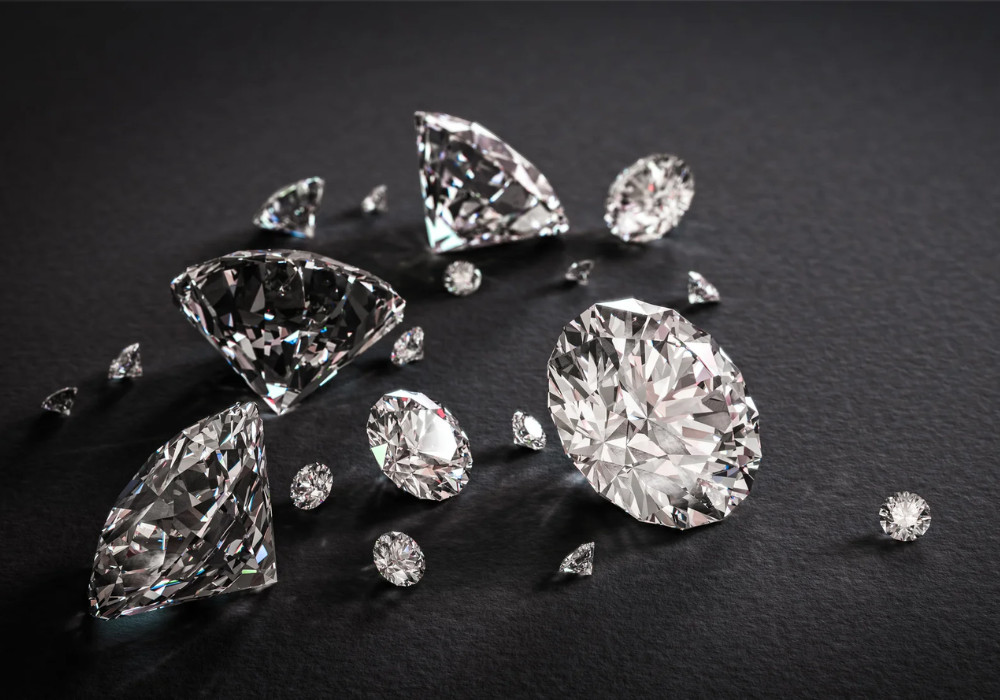
Lab-grown diamonds, also known as synthetic diamonds or cultured diamonds, are diamonds that are created in a laboratory instead of being formed naturally in the Earth’s crust. They possess the same chemical composition, physical properties, and optical characteristics as natural diamonds. However, the key difference lies in their origin and the process by which they are formed.
Lab-grown diamonds are created using advanced technologies that simulate the natural diamond-growing conditions. There are two main methods used to grow lab-grown diamonds: Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) and High Pressure High Temperature (HPHT).
- Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD): The CVD process involves placing a diamond seed, a small piece of diamond, in a sealed chamber. The chamber is then filled with a carbon-rich gas, typically methane. By applying high-frequency microwave energy, the gas is ionized, breaking down the molecular bonds and releasing carbon atoms. These carbon atoms settle on the diamond seed and gradually crystallize, layer by layer, forming a larger diamond. This method allows for precise control over the growth process and can produce high-quality diamonds.
- High Pressure High Temperature (HPHT): The HPHT process involves placing a diamond seed in a press along with a carbon source, such as graphite, and metal catalysts. The press applies extreme pressure, up to 5 GigaPascals, and temperatures exceeding 1500 degrees Celsius. Under these conditions, the carbon dissolves into a molten metal catalyst. As the temperature and pressure are gradually reduced, the carbon crystallizes around the diamond seed, resulting in the growth of a larger diamond. This method replicates the natural diamond formation process, but in a shorter time frame.
Lab-grown diamonds can be produced in various sizes, colors, and clarities, just like natural diamonds. They undergo the same cutting and polishing processes as natural diamonds to enhance their brilliance and appearance. They are then graded using the same industry standards as natural diamonds based on the 4Cs: carat weight, color, clarity, and cut.
Lab-grown diamonds offer several advantages over natural diamonds. First, they are more environmentally friendly since they require minimal mining and have a lower carbon footprint. They also provide a more traceable and transparent supply chain, ensuring ethical sourcing and reducing the risk of conflict diamonds. Additionally, lab-grown diamonds are often priced more competitively than natural diamonds, making them an appealing option for those seeking high-quality diamonds at a lower cost.
It’s important to note that lab-grown diamonds are not simulants or imitations; they are real diamonds with the same physical and chemical properties as natural diamonds. They are a legitimate alternative for those who value sustainability, ethical considerations, and affordability without compromising on the beauty and quality of a diamond.

Lab-grown diamonds, also known as synthetic or cultured diamonds, offer several fascinating aspects that set them apart from natural diamonds. Here are some intriguing facts about lab-grown diamonds:
Identical Composition:
Lab-grown diamonds have the same chemical composition as natural diamonds. Both are made of carbon atoms arranged in a crystal lattice structure, resulting in identical physical and chemical properties.
Optically and Physically Indistinguishable:
Lab-grown diamonds possess the same optical and physical characteristics as natural diamonds. They exhibit the same brilliance, sparkle, and hardness, making them visually and mechanically indistinguishable from natural diamonds.
Growth Customization:
Unlike natural diamonds, lab-grown diamonds can be grown with specific characteristics tailored to meet consumer demands. This includes controlling factors such as size, color, clarity, and even specific fluorescence properties.
Sustainable and Environmentally Friendly:
Lab-grown diamonds have a significantly lower environmental impact compared to traditional diamond mining. They require fewer natural resources and do not involve harmful mining practices, reducing land disruption and the release of pollutants into the environment.
Ethical Sourcing:
Lab-grown diamonds offer a transparent and traceable supply chain. Since they are created in a controlled laboratory environment, there are no concerns about human rights violations or the involvement of conflict diamonds, providing peace of mind for socially conscious consumers.
Greater Affordability:
Lab-grown diamonds are often more affordable than natural diamonds. Their pricing is generally lower due to reduced production costs and a more controlled supply chain. This accessibility makes high-quality diamonds more attainable for a wider range of consumers.
Versatile Colors:
Lab-grown diamonds can exhibit a wide range of colors, including fancy colors, such as blue, yellow, pink, and green. The controlled growth process allows for the creation of diamonds with specific color saturations and hues.
Research and Technological Advancements:
The production of lab-grown diamonds has driven significant advancements in materials science and diamond-growing technologies. These innovations have potential applications beyond jewelry, including in fields such as electronics, optics, and quantum computing.
Symbolic Meaning:
Lab-grown diamonds can carry unique symbolic meaning for individuals who appreciate the science, innovation, and sustainability behind their creation. They represent a modern approach to luxury and personal expression.
Coexistence with Natural Diamonds:
Lab-grown diamonds complement rather than compete with natural diamonds. They offer consumers an alternative choice while coexisting within the broader diamond market. The availability of lab-grown diamonds has sparked discussions about the value and significance of diamonds, encouraging greater transparency and ethical considerations throughout the diamond industry.
These fascinating aspects of lab-grown diamonds make them an intriguing and appealing option for consumers who value sustainability, customization, and technological advancements while still desiring the beauty and allure of a diamond.