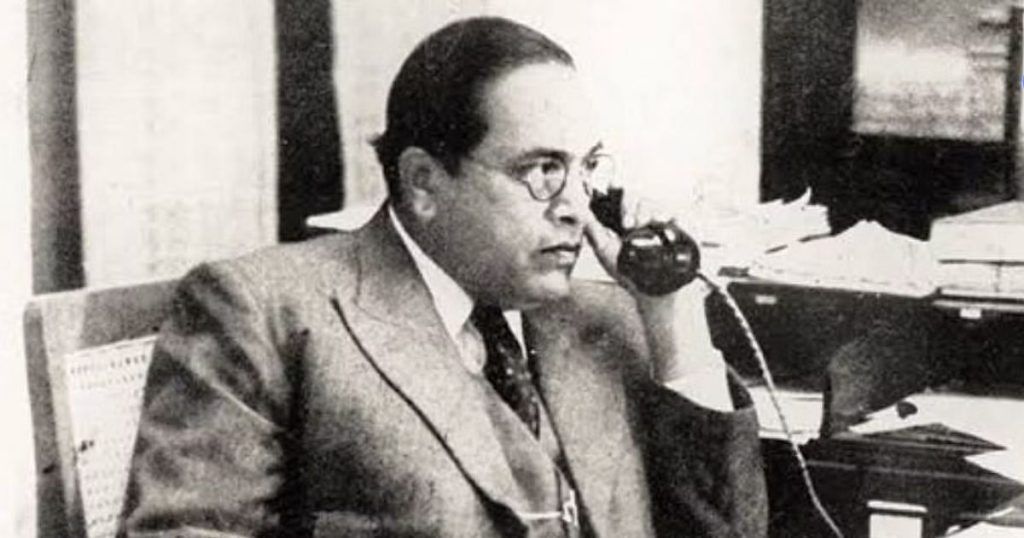
Bhimrao Ramji Ambedkar, commonly known as Baba Saheb Ambedkar, was born in Mhow, Madhya Pradesh, India, on April 14, 1891. He was an excellent student, getting doctorates from both London University and Columbia University. He established a reputation as a scholar through his work in law, economics, and political science. In his early career, he worked as an editor, economist, professor, and activist against caste prejudice against Dalits. Dr. B.R. Ambedkar’s later career included political involvement.
Ambedkar History
Dr. B.R.Ambedkar was born in the Madhya Pradesh town of Mhow. Ramji Makoji Sakpal’s father was an army officer in the British India army. Dr. B.R.Ambedkar was his father’s thirteenth son. His mother’s name was Bhimabai Sakpal. His family was of Marathi origin, hailing from the town of Ambawade. Dr. B. R. Ambedkar was born as a Dalit and was treated as such. He was regularly subjected to social and economic discrimination. Despite attending school, Ambedkar and other Dalit kids were considered as untouchables. They were isolated from another set of youngsters from a different caste and received no attention from the teachers. They were not even permitted to sit with other students for their drinking water.
He used to drink water with the help of the peon as he and other Dalit students were not allowed to touch anything. His father retired in 1894 and his mother passed away 2 years after they moved to Satara. Of all his brothers and sisters, Ambedkar was the only one who passed his examination and went to high school. Later in high school, his school, a Brahmin teacher, changed his surname from Ambadawekar, which was given by his father to Ambedkar in records. This shows the level of discrimination that was done on Dalits. Dr. Bhim Rao Ambedkar EducationIn 1897, Ambedkar became the only untouchable to get enrolled at the Elphinstone High School. In 1906, Ambedkar, who was 15 years old, married a 9 years old named Ramabai.
The marriage was done by the couple’s parents as per the rituals. In 1912, he obtained his degree in political science and economics from Bombay University and was employed by the Baroda state government. In 1913, Ambedkar moved to the United States as he was awarded a scholarship for three years by Sayajirao Gaekwad three. The scholarship was designed to provide opportunities for post-graduate education at Columbia University in New York City. In 1915, he majored in Economics, Sociology, History, Philosophy, and Anthropology. In 1917, he completed his master’s degree and wrote a thesis on “The problem of the rupee- its origin and solution,” and in 1923, he completed a D.Sc in Economics, which was awarded by the University of London.
The birthday of Dr. B. R. Ambedkar, or Bhimrao Ramji Ambedkar, is on April 14 as he was born on that day in Mhow, India, in the year 1891 and died on December 6, 1956, in New Delhi. His mother’s name was Bhimabai and father’s name was Ramji Sakpal. He was born in an army cantonment in Madhya Pradesh as his father was an army subedar. Once his father retired, they moved to Satara and that’s where his mother passed away. His father remarried four years after the death of his mother and the family relocated to Bombay. When Dr. Bhimrao Ambedkar was 15 years old, he was married to Ramabai, who was a 9-year-old girl, in 1906. In 1912, the father of Ambedkar died in Bombay.
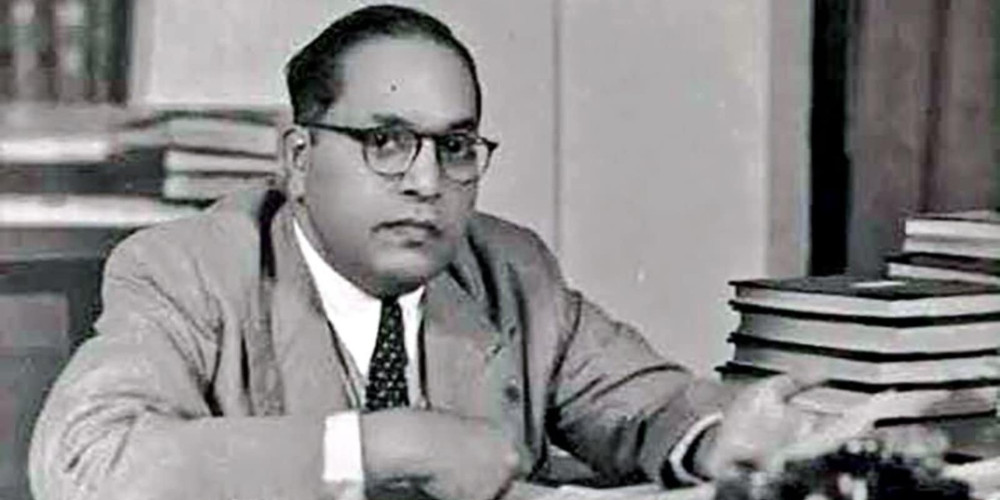

Ambedkar had a difficult time in his childhood because he always faced caste discrimination. He belonged to a Dalit family and Dalits were considered “untouchables,” a low caste. When Ambedkar was in an army school, he faced discrimination there as well. Due to this, teachers usually made a separate arrangement for low caste students so that they are not mixed with high caste students like Brahmins. Sometimes, Ambedkar and other low caste students were even asked to sit outside the classroom by the teachers as they feared it might cause problems if low caste students were mixed with high-class students.
The problem of caste discrimination didn’t end for Ambedkar even when he was enrolled in a local school in Satara. This discrimination seemed to be following him. When he came back from America, the King of Baroda appointed him as his defense secretary. Even being in such a high position, he was called ‘untouchable’ by his upper-class officials.
Ambedkar’s Involvement during Independence
Ambedkar was involved in campaigning and negotiation of India’s Independence. After Independence, he became the chairman of the drafting committee of the Indian constitution. After India’s Independence, he was the first minister of law and justice and is considered to be the architect of the constitution of India. In 1956 he converted to Buddhism, resulting in the mass conversion of Dalits. In 1948, Ambedkar suffered from diabetes. After fighting diabetes for almost seven years, Ambedkar passed away in his sleep on December 6 1956 at his home.
Education Of Dr B. R. Ambedkar
In 1908, Ambedkar passed his tenth class from the Elphinstone High School. He graduated from Bombay University in 1912 and his subjects included political studies and economics. Ambedkar was an intelligent student and cleared all his exams without much problem. Gaekwad ruler of, Sahyaji Rao III was so impressed with him that he gave a scholarship of 25 rupees per month to Ambedkar. Ambedkar used all that money to continue his studies outside India. He applied for Columbia University in New York to complete his master’s degree in Economics.
He was selected in that university and completed his master’s degree in 1915 and this is the time when he gave his thesis called ‘Ancient Indian Commerce. In 1916, he started working on his new thesis, ‘The problem of the rupee: Its origin and its solution’ and this was the time when he applied for the London School of Economics and got selected. In this thesis, he was also helped by Governor Lord Sydenham. In Sydenham College of Commerce and Economics, he became a political science professor, but he decided to continue his further studies and went to England. He completed his Ph.D. degree in 1927 in Economics and was awarded a Doctorate by the University of Columbia in the same year.
Achievements of Dr B. R. Ambedkar
Ambedkar played a key role in the formation of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) in 1935. Back in 1955, he was the first person to propose the partition of Madhya Pradesh and Bihar for better government. He also wanted to make Sanskrit the Indian union’s official language and he took part in the ‘Lok Sabha’ election twice but failed to win on both occasions. ‘Waiting for a Visa,’ his autobiography, is used as a textbook at Columbia University. He was opposed to the principle of employment and constituency reservation and didn’t want the system to exist at all. He was the first Indian to earn a Ph.D. degree outside of India. Ambedkar was the one who pushed for a reduction in India’s working hours from 14 to eight hours a day. He was a vocal opponent of the Indian constitution’s ‘Article 370,’ which granted the state of Jammu and Kashmir special status.
In 1916, Dr. B.R.Ambedkar worked as the defense secretary for the princely state of Baroda. As he was a Dalit, wor was not easy. He was ridiculed by the people and often ignored. After continuous caste discrimination, he quit his job as the defense secretary and took up jobs as a private tutor and accountant. He later established a consulting firm, but it failed to flourish. The reason has been that he was a Dalit. He finally got a job as a teacher at the Sydenham College of Commerce and Economics in Mumbai. As Ambedkar was a victim of caste discrimination, he thrived on uplifting the pitiable state of the untouchables in society. He founded a weekly journal called “Mooknayak,” which enabled him to criticize the beliefs of the Hindus. He was passionate about eradicating the practice of caste discrimination in India which led him to establish “Bahishkrit Hitakarni Sabha.”

The main goal of the organization was to provide education to the backward classes. In 1927, he continuously worked against untouchability. He followed the footsteps of Gandhi and led a Satyagraha movement. The untouchables were denied access to the main source of drinking water and entry in Temples. He fought for the rights of the untouchables. In 1932, the “Poona Pact” was formed that allowed reservation for the depressed class in the regional legislative assembly and central council states. In 1935, he founded the “Independent labor party,” which secured fourteen seats in the Bombay election.
In 1935, he published books such as ‘The Annihilation of Caste,’ which questioned orthodox Hindu beliefs, and the very next year, he published another book by the name ‘Who Were the Shudras?’ in which he explained how the untouchables were formed. After India’s Independence, he served on the board of the defense advisory committee and as the minister for labor for the ‘viceroy’s executive council.’His dedication towards the work earned him the chair of India’s first law minister. He was the first chairman of the drafting committee of the Constitution of India.
He also established the finance committee of India. It was through his policies the nation progressed both economically and socially. In 1951, ‘The Hindu Code Bill’ was proposed to him, which he later rejected and resigned from the Cabinet. He contested for the seat of Likh Sabha but was defeated. He was later appointed to the Rajya Sabha and remained a member of the Rajya Sabha until his death in 1955.
Thoughts and Opinions
B.R. Ambedkar was a leading social reformer and an activist who dedicated his entire life to the betterment of the Dalits and other socially backward classes of India. Ambedkar continuously fought for the eradication of caste discrimination that had spread like a disease in Indian society. As he was born in a socially backward family, Ambedkar was a Dalit who was a victim of caste discrimination and inequality. However, against all odds, Ambedkar became the first Dalit to complete higher education. He then went on and completed college and got a doctorate in economics from London University. He entered politics entirely, aiming to fight for the rights of the backward classes and against the inequality practiced in society. After India became independent, he went on to become the first law minister of free India and the chief architect of the ‘Constitution of India.’Later in 1956, he converted to Buddhism, as he considered it to be ‘the most scientific religion.’
Within 2 months of the conversion anniversary, Ambedkar died of diabetes in 1956.ConclusionBhimrao Ramji Ambedkar, popularly known as Baba Saheb, was a jurist, politician, economist, writer, editor. He was a Dalit who was a usual subject to caste discrimination. He was not allowed to eat with other caste children or even drink water at school. His story is the best example of determination and showcases how education can change the fortune of anyone. A child who was subject to caste discrimination went on to become a man who was the architect of Independent India’s constitution. A story is written in heaven’s which is the best example of not giving up on yourself even if the odds are against you.